This page was generated from
dis_voronoi_example.py.
It's also available as a notebook.
Voronoi Grid and MODFLOW 6 Flow and Transport Example
First set the path and import the required packages. The flopy path doesn’t have to be set if you install flopy from a binary installer. If you want to run this notebook, you have to set the path to your own flopy path.
[1]:
import os
import sys
from pathlib import Path
from pprint import pformat
from tempfile import TemporaryDirectory
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import LineString, Point
import flopy
from flopy.discretization import VertexGrid
from flopy.utils.triangle import Triangle as Triangle
from flopy.utils.voronoi import VoronoiGrid
temp_dir = TemporaryDirectory()
workspace = Path(temp_dir.name)
print(sys.version)
print(f"numpy version: {np.__version__}")
print(f"matplotlib version: {mpl.__version__}")
print(f"flopy version: {flopy.__version__}")
3.12.2 | packaged by conda-forge | (main, Feb 16 2024, 20:50:58) [GCC 12.3.0]
numpy version: 1.26.4
matplotlib version: 3.8.4
flopy version: 3.7.0.dev0
Use Triangle to Generate Points for Voronoi Grid
[2]:
# set domain extents
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 2000.0
ymin = 0.0
ymax = 1000.0
# set minimum angle
angle_min = 30
# set maximum area
area_max = 1000.0
delr = area_max**0.5
ncol = xmax / delr
nrow = ymax / delr
nodes = ncol * nrow
print("equivalent delr: ", delr)
print("equivalent nodes, ncol, nrow: ", int(nodes), ncol, nrow)
equivalent delr: 31.622776601683793
equivalent nodes, ncol, nrow: 2000 63.245553203367585 31.622776601683793
[3]:
tri = Triangle(maximum_area=area_max, angle=angle_min, model_ws=workspace)
poly = np.array(((xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (xmin, ymax)))
tri.add_polygon(poly)
tri.build(verbose=False)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect="equal")
pc = tri.plot(ax=ax)

Create and Plot FloPy Voronoi Grid
The Flopy VoronoiGrid class can be used to generate voronoi grids using the scipy.spatial.Voronoi class. The VoronoiGrid class is a thin wrapper that makes sure edge cells are closed and provides methods for obtaining the information needed to make FloPy MODFLOW models. It works by passing in the flopy Triangle object generated in the previous cell.
[4]:
voronoi_grid = VoronoiGrid(tri)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect="equal")
voronoi_grid.plot(ax=ax, facecolor="none")
[4]:
<Axes: title={'center': 'ncells: 1692; nverts: 3750'}>

Use the VertexGrid Representation to Identify Boundary Cells
[5]:
gridprops = voronoi_grid.get_gridprops_vertexgrid()
vgrid = flopy.discretization.VertexGrid(**gridprops, nlay=1)
ibd = np.zeros(vgrid.ncpl, dtype=int)
gi = flopy.utils.GridIntersect(vgrid)
# identify cells on left edge
line = LineString([(xmin, ymin), (xmin, ymax)])
cells0 = gi.intersect(line)["cellids"]
cells0 = np.array(list(cells0))
ibd[cells0] = 1
# identify cells on right edge
line = LineString([(xmax, ymin), (xmax, ymax)])
cells1 = gi.intersect(line)["cellids"]
cells1 = np.array(list(cells1))
ibd[cells1] = 2
# identify cell for a constant concentration condition
point = Point((500, 500))
cells2 = gi.intersect(point)["cellids"]
cells2 = np.array(list(cells2))
ibd[cells2] = 3
if True:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect="equal")
pmv = flopy.plot.PlotMapView(modelgrid=vgrid)
pmv.plot_array(ibd)

Create Run and Post Process a MODFLOW 6 Flow Model
[6]:
name = "mf"
sim_ws = os.path.join(workspace, "flow")
sim = flopy.mf6.MFSimulation(
sim_name=name, version="mf6", exe_name="mf6", sim_ws=sim_ws
)
tdis = flopy.mf6.ModflowTdis(
sim, time_units="DAYS", perioddata=[[1.0, 1, 1.0]]
)
gwf = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwf(sim, modelname=name, save_flows=True)
ims = flopy.mf6.ModflowIms(
sim,
print_option="SUMMARY",
complexity="complex",
outer_dvclose=1.0e-8,
inner_dvclose=1.0e-8,
)
disv_gridprops = voronoi_grid.get_disv_gridprops()
nlay = 1
top = 1.0
botm = [0.0]
disv = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwfdisv(
gwf, nlay=nlay, **disv_gridprops, top=top, botm=botm
)
npf = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwfnpf(
gwf,
xt3doptions=[(True)],
k=10.0,
save_saturation=True,
save_specific_discharge=True,
)
ic = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwfic(gwf)
chdlist = []
for icpl in cells0:
chdlist.append([(0, icpl), 1.0])
for icpl in cells1:
chdlist.append([(0, icpl), 0.0])
chd = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwfchd(gwf, stress_period_data=chdlist)
oc = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwfoc(
gwf,
budget_filerecord=f"{name}.bud",
head_filerecord=f"{name}.hds",
saverecord=[("HEAD", "ALL"), ("BUDGET", "ALL")],
printrecord=[("HEAD", "LAST"), ("BUDGET", "LAST")],
)
sim.write_simulation()
success, buff = sim.run_simulation(report=True, silent=True)
assert success, pformat(buff)
head = gwf.output.head().get_data()
bdobj = gwf.output.budget()
spdis = bdobj.get_data(text="DATA-SPDIS")[0]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15))
ax = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect="equal")
pmv = flopy.plot.PlotMapView(gwf)
pmv.plot_array(head, cmap="jet", alpha=0.5)
pmv.plot_vector(spdis["qx"], spdis["qy"], alpha=0.25)
writing simulation...
writing simulation name file...
writing simulation tdis package...
writing solution package ims_-1...
writing model mf...
writing model name file...
writing package disv...
writing package npf...
writing package ic...
writing package chd_0...
INFORMATION: maxbound in ('gwf6', 'chd', 'dimensions') changed to 62 based on size of stress_period_data
writing package oc...
[6]:
<matplotlib.quiver.Quiver at 0x7f5512cadc10>

Create Run and Post Process a MODFLOW 6 Transport Model
[7]:
name = "mf"
sim_ws = os.path.join(workspace, "transport")
sim = flopy.mf6.MFSimulation(
sim_name=name, version="mf6", exe_name="mf6", sim_ws=sim_ws
)
tdis = flopy.mf6.ModflowTdis(
sim, time_units="DAYS", perioddata=[[100 * 365.0, 100, 1.0]]
)
gwt = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwt(sim, modelname=name, save_flows=True)
ims = flopy.mf6.ModflowIms(
sim,
print_option="SUMMARY",
complexity="simple",
linear_acceleration="bicgstab",
outer_dvclose=1.0e-6,
inner_dvclose=1.0e-6,
)
disv_gridprops = voronoi_grid.get_disv_gridprops()
nlay = 1
top = 1.0
botm = [0.0]
disv = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtdisv(
gwt, nlay=nlay, **disv_gridprops, top=top, botm=botm
)
ic = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtic(gwt, strt=0.0)
sto = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtmst(gwt, porosity=0.2)
adv = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtadv(gwt, scheme="TVD")
dsp = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtdsp(gwt, alh=5.0, ath1=0.5)
sourcerecarray = [()]
ssm = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtssm(gwt, sources=sourcerecarray)
cnclist = [
[(0, cells2[0]), 1.0],
]
cnc = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtcnc(
gwt, maxbound=len(cnclist), stress_period_data=cnclist, pname="CNC-1"
)
pd = [
("GWFHEAD", "../flow/mf.hds"),
("GWFBUDGET", "../flow/mf.bud"),
]
fmi = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtfmi(gwt, packagedata=pd)
oc = flopy.mf6.ModflowGwtoc(
gwt,
budget_filerecord=f"{name}.cbc",
concentration_filerecord=f"{name}.ucn",
saverecord=[("CONCENTRATION", "ALL"), ("BUDGET", "ALL")],
)
sim.write_simulation()
success, buff = sim.run_simulation(report=True, silent=True)
assert success, pformat(buff)
conc = gwt.output.concentration().get_data()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect="equal")
pmv = flopy.plot.PlotMapView(gwf)
c = pmv.plot_array(conc, cmap="jet")
pmv.contour_array(conc, levels=(0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1), colors="y")
plt.colorbar(c, shrink=0.5)
writing simulation...
writing simulation name file...
writing simulation tdis package...
writing solution package ims_-1...
writing model mf...
writing model name file...
writing package disv...
writing package ic...
writing package mst...
writing package adv...
writing package dsp...
writing package ssm...
writing package cnc-1...
writing package fmi...
writing package oc...
[7]:
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar at 0x7f551335b7a0>

Building Voronoi Grid Examples
Irregular Domain Boundary
[8]:
domain = [
[1831.381546, 6335.543757],
[4337.733475, 6851.136153],
[6428.747084, 6707.916043],
[8662.980804, 6493.085878],
[9350.437333, 5891.561415],
[9235.861245, 4717.156511],
[8963.743036, 3685.971717],
[8691.624826, 2783.685023],
[8047.13433, 2038.94045],
[7416.965845, 578.0953252],
[6414.425073, 105.4689614],
[5354.596258, 205.7230386],
[4624.173696, 363.2651598],
[3363.836725, 563.7733141],
[1330.11116, 1809.788273],
[399.1804436, 2998.515188],
[914.7728404, 5132.494831],
]
area_max = 100.0**2
tri = Triangle(maximum_area=area_max, angle=30, model_ws=workspace)
poly = np.array(domain)
tri.add_polygon(poly)
tri.build(verbose=False)
vor = VoronoiGrid(tri)
gridprops = vor.get_gridprops_vertexgrid()
voronoi_grid = VertexGrid(**gridprops, nlay=1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
voronoi_grid.plot(ax=ax)
[8]:
<matplotlib.collections.LineCollection at 0x7f5512df3a70>

Simple Rectangular Domain
[9]:
xmin = 0.0
xmax = 2.0
ymin = 0.0
ymax = 1.0
area_max = 0.001
tri = Triangle(maximum_area=area_max, angle=30, model_ws=workspace)
poly = np.array(((xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (xmin, ymax)))
tri.add_polygon(poly)
tri.build(verbose=False)
vor = VoronoiGrid(tri)
gridprops = vor.get_gridprops_vertexgrid()
voronoi_grid = VertexGrid(**gridprops, nlay=1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
voronoi_grid.plot(ax=ax)
[9]:
<matplotlib.collections.LineCollection at 0x7f5523d319d0>

Circular Grid
[10]:
theta = np.arange(0.0, 2 * np.pi, 0.2)
radius = 100.0
x = radius * np.cos(theta)
y = radius * np.sin(theta)
circle_poly = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(x, y)]
tri = Triangle(maximum_area=5, angle=30, model_ws=workspace)
tri.add_polygon(circle_poly)
tri.build(verbose=False)
vor = VoronoiGrid(tri)
gridprops = vor.get_gridprops_vertexgrid()
voronoi_grid = VertexGrid(**gridprops, nlay=1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
voronoi_grid.plot(ax=ax)
[10]:
<matplotlib.collections.LineCollection at 0x7f5512e000e0>

Circular Grid with Hole
[11]:
theta = np.arange(0.0, 2 * np.pi, 0.2)
radius = 30.0
x = radius * np.cos(theta) + 25.0
y = radius * np.sin(theta) + 25.0
inner_circle_poly = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(x, y)]
tri = Triangle(maximum_area=10, angle=30, model_ws=workspace)
tri.add_polygon(circle_poly)
tri.add_polygon(inner_circle_poly)
tri.add_hole((25, 25))
tri.build(verbose=False)
vor = VoronoiGrid(tri)
gridprops = vor.get_gridprops_vertexgrid()
voronoi_grid = VertexGrid(**gridprops, nlay=1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
voronoi_grid.plot(ax=ax)
[11]:
<matplotlib.collections.LineCollection at 0x7f55127f6210>

Regions with Different Refinement
[12]:
active_domain = [(0, 0), (100, 0), (100, 100), (0, 100)]
area1 = [(10, 10), (40, 10), (40, 40), (10, 40)]
area2 = [(60, 60), (80, 60), (80, 80), (60, 80)]
tri = Triangle(angle=30, model_ws=workspace)
tri.add_polygon(active_domain)
tri.add_polygon(area1)
tri.add_polygon(area2)
tri.add_region((1, 1), 0, maximum_area=100) # point inside active domain
tri.add_region((11, 11), 1, maximum_area=10) # point inside area1
tri.add_region((61, 61), 2, maximum_area=3) # point inside area2
tri.build(verbose=False)
vor = VoronoiGrid(tri)
gridprops = vor.get_gridprops_vertexgrid()
voronoi_grid = VertexGrid(**gridprops, nlay=1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
voronoi_grid.plot(ax=ax)
[12]:
<matplotlib.collections.LineCollection at 0x7f55113d5190>

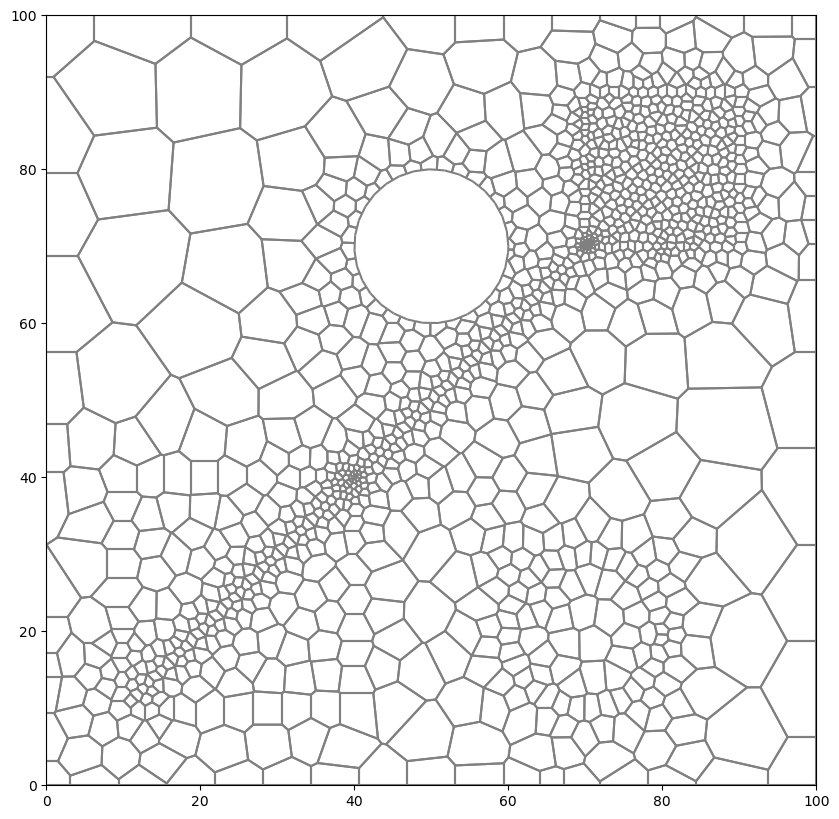
Regions with Different Refinement and Hole
[13]:
active_domain = [(0, 0), (100, 0), (100, 100), (0, 100)]
area1 = [(10, 10), (40, 10), (40, 40), (10, 40)]
area2 = [(70, 70), (90, 70), (90, 90), (70, 90)]
tri = Triangle(angle=30, model_ws=workspace)
# requirement that active_domain is first polygon to be added
tri.add_polygon(active_domain)
# requirement that any holes be added next
theta = np.arange(0.0, 2 * np.pi, 0.2)
radius = 10.0
x = radius * np.cos(theta) + 50.0
y = radius * np.sin(theta) + 70.0
circle_poly0 = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(x, y)]
tri.add_polygon(circle_poly0)
tri.add_hole((50, 70))
# Add a polygon to force cells to conform to it
theta = np.arange(0.0, 2 * np.pi, 0.2)
radius = 10.0
x = radius * np.cos(theta) + 70.0
y = radius * np.sin(theta) + 20.0
circle_poly1 = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(x, y)]
tri.add_polygon(circle_poly1)
# tri.add_hole((70, 20))
# add line through domain to force conforming cells
line = [(x, x) for x in np.linspace(11, 89, 100)]
tri.add_polygon(line)
# then regions and other polygons should follow
tri.add_polygon(area1)
tri.add_polygon(area2)
tri.add_region((1, 1), 0, maximum_area=100) # point inside active domain
tri.add_region((11, 11), 1, maximum_area=10) # point inside area1
tri.add_region((70, 70), 2, maximum_area=1) # point inside area2
tri.build(verbose=False)
vor = VoronoiGrid(tri)
gridprops = vor.get_gridprops_vertexgrid()
voronoi_grid = VertexGrid(**gridprops, nlay=1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
voronoi_grid.plot(ax=ax)
[13]:
<matplotlib.collections.LineCollection at 0x7f5510cf7fe0>
[14]:
try:
# ignore PermissionError on Windows
temp_dir.cleanup()
except:
pass